
Starting with Patient Safety and Infection Control, this opening paragraph aims to grab the readers’ attention and provide a glimpse into the crucial aspects of ensuring health and safety in healthcare environments.
The following paragraph will delve deeper into the intricacies of patient safety, infection control, hand hygiene, and personal protective equipment.
Patient Safety
Patient safety is a critical aspect of healthcare that involves preventing harm to patients during their medical care. It is essential for healthcare providers to prioritize patient safety to ensure positive health outcomes and reduce the risk of medical errors.
Importance of Patient Safety
- Ensures quality healthcare delivery
- Builds trust between patients and healthcare providers
- Reduces healthcare costs associated with medical errors
Common Patient Safety Issues
- Medication errors
- Healthcare-associated infections
- Communication breakdowns
Role of Healthcare Professionals
- Following evidence-based practices
- Effective communication with patients and colleagues
- Continuous training and education on patient safety protocols
Strategies to Enhance Patient Safety Practices
- Implementing electronic health records for accurate information sharing
- Standardizing protocols and procedures across healthcare facilities
- Encouraging a culture of reporting and learning from near-misses
Infection Control

Infection control is the set of practices and procedures designed to prevent the spread of infectious diseases in healthcare settings. It is crucial in maintaining patient safety and reducing the risk of healthcare-associated infections.
Common Sources of Healthcare-Associated Infections
- Poor hand hygiene: Failure to wash hands properly between patient interactions can lead to the spread of infections.
- Inadequate sterilization and disinfection of medical equipment: Improper cleaning of instruments can result in the transmission of pathogens.
- Contaminated surfaces: Surfaces in healthcare facilities can harbor bacteria and viruses, posing a risk of infection to patients.
- Improper waste disposal: Incorrect disposal of medical waste can contribute to the spread of infections.
Principles of Infection Control Measures
- Hand hygiene: Regular and thorough handwashing is essential to prevent the transmission of pathogens.
- Use of personal protective equipment (PPE): Healthcare workers should wear appropriate PPE, such as gloves and masks, to protect themselves and patients.
- Cleaning and disinfection: Proper cleaning and disinfection of surfaces and equipment help eliminate pathogens.
- Isolation precautions: Patients with certain infectious diseases should be isolated to prevent the spread of infection to others.
Impact of Effective Infection Control on Patient Outcomes
Effective infection control measures have a significant impact on patient outcomes by reducing the incidence of healthcare-associated infections. This leads to improved patient safety, shorter hospital stays, and lower healthcare costs. Additionally, it helps prevent the spread of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, which are a growing concern in healthcare settings.
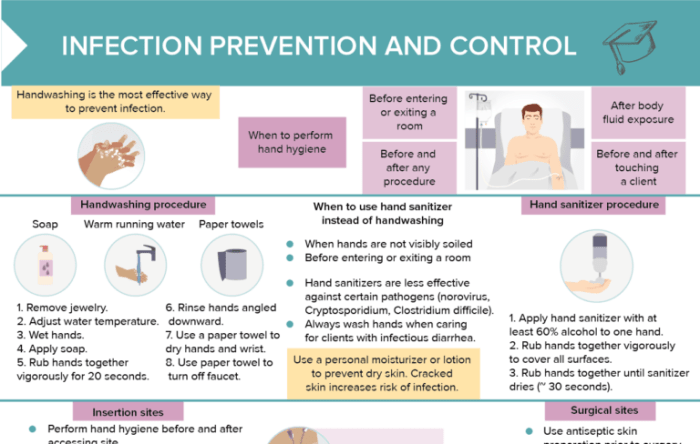
Hand Hygiene
Proper hand hygiene is crucial in preventing the spread of infections, especially in healthcare settings where patients are vulnerable to illnesses. By washing hands effectively, healthcare workers can reduce the risk of transmitting harmful pathogens and keeping both themselves and patients safe.
Hand Hygiene Techniques
- Regular Handwashing: The most basic and effective method to remove dirt, germs, and harmful bacteria from hands. Use soap and water, lather for at least 20 seconds, and rinse thoroughly.
- Hand Sanitizing: When soap and water are not readily available, alcohol-based hand sanitizers can be used to kill germs and disinfect hands. Make sure to cover all surfaces of the hands and rub until dry.
- Surgical Hand Antisepsis: Healthcare workers performing surgical procedures need to follow a specific hand hygiene protocol to ensure a sterile environment. This involves using antimicrobial soap or hand rub before donning sterile gloves.
Key Moments for Hand Hygiene Compliance
- Before and after patient contact: Healthcare workers should clean their hands before touching a patient to prevent the spread of germs and after to avoid transmitting any potential pathogens to others.
- Before aseptic procedures: Prior to performing any sterile procedures, proper hand hygiene is essential to maintain asepsis and prevent infections.
- After contact with body fluids: After exposure to bodily fluids or contaminated surfaces, it is crucial to wash hands thoroughly to prevent the spread of infections.
Best Practices for Hand Hygiene in Healthcare Settings
- Encourage a culture of hand hygiene compliance: Healthcare facilities should prioritize and promote hand hygiene practices among staff members through education and reinforcement.
- Provide easy access to hand hygiene products: Ensure that soap, water, hand sanitizers, and gloves are readily available in all patient care areas to facilitate proper hand hygiene.
- Regular monitoring and feedback: Implement systems to monitor hand hygiene compliance and provide feedback to healthcare workers to encourage adherence to best practices.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Wearing Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is crucial in preventing the spread of infections, especially in healthcare settings where exposure to pathogens is high. PPE serves as a barrier between the wearer and infectious materials, reducing the risk of contamination.
Types of PPE and Their Uses
- Gloves: Used to protect hands from contamination and should be changed between patients or tasks.
- Masks: Help prevent respiratory droplets from entering the mouth and nose. N95 respirators are specifically designed to filter out airborne particles.
- Gowns: Cover clothing and skin to prevent contamination from fluids or pathogens.
- Face shields or goggles: Protect the eyes, nose, and mouth from splashes or sprays.
Proper Disposal of PPE
- Dispose of used PPE in designated bins or containers to prevent cross-contamination.
- Follow proper disposal protocols to ensure the safe removal of contaminated PPE.
- Do not reuse disposable PPE to maintain its effectiveness in preventing infections.
Guidelines for Healthcare Workers
- Choose the appropriate PPE based on the type of exposure and level of risk.
- Ensure a proper fit of PPE to maximize protection and minimize gaps.
- Regularly inspect and replace damaged or soiled PPE to maintain its integrity.
- Practice proper donning and doffing techniques to avoid self-contamination.
Wrapping up the discussion on Patient Safety and Infection Control, we emphasize the significance of these practices in safeguarding patients and healthcare workers, ultimately leading to better outcomes and overall well-being.
FAQ Overview
What are some common patient safety issues?
Common patient safety issues include medication errors, miscommunication between healthcare providers, and hospital-acquired infections.
How does proper hand hygiene prevent infections?
Proper hand hygiene reduces the transmission of harmful pathogens from surfaces to patients, preventing the spread of infections.
Why is selecting and using PPE correctly important?
Selecting and using PPE correctly ensures that healthcare workers are adequately protected from exposure to infectious agents, minimizing the risk of infection.





