Medical Errors and Patient Safety sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail with a focus on ensuring healthcare quality and patient well-being.
This comprehensive discussion covers the various aspects of medical errors, their impact on patient safety, and strategies to prevent them, providing valuable insights for healthcare professionals and patients alike.
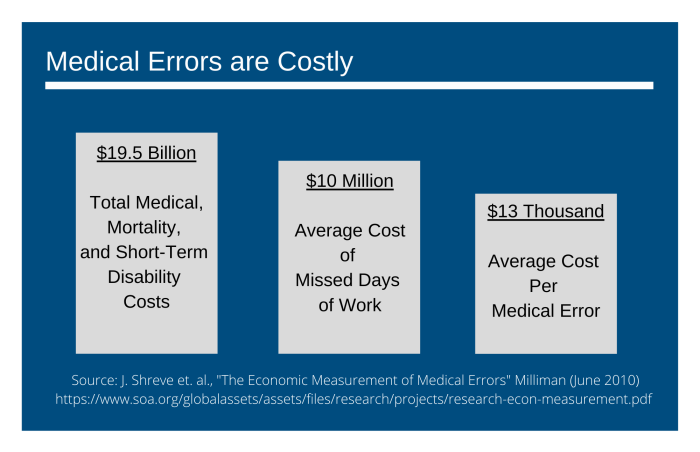
Medical Errors

Medical errors are mistakes made in healthcare settings that can result in harm to patients. These errors can occur at any point in the patient care process, from diagnosis to treatment. Examples of medical errors include misdiagnosis, medication errors, surgical errors, and communication breakdowns between healthcare providers.
Common Causes of Medical Errors
- Communication breakdowns between healthcare providers
- Fatigue and burnout among healthcare staff
- Inadequate training or supervision
- High patient volume leading to rushed care
- Equipment failure or malfunction
Impact of Medical Errors on Patient Safety and Outcomes
Medical errors can have serious consequences for patients, including prolonged hospital stays, disability, and even death. They can also erode patient trust in the healthcare system and lead to increased healthcare costs. Ensuring patient safety and preventing medical errors is crucial for improving healthcare outcomes.
Strategies to Prevent Medical Errors in Healthcare Settings
- Implementing electronic health records to improve communication and reduce errors
- Standardizing procedures and protocols to ensure consistency in care
- Encouraging a culture of open communication and reporting of errors
- Providing ongoing training and education for healthcare staff
- Engaging patients in their care and encouraging them to ask questions
Types of Medical Errors

Medical errors can take various forms and can occur at different stages of patient care. Understanding the different types of medical errors, along with the factors contributing to them, is crucial in improving patient safety.
Medication Errors
Medication errors are one of the most common types of medical errors and can happen during prescribing, dispensing, or administering medications. Factors such as look-alike or sound-alike medications, improper dosage calculations, and miscommunication between healthcare providers can contribute to medication errors. For example, a nurse administering the wrong medication due to illegible handwriting on a prescription.
Surgical Errors
Surgical errors occur during surgical procedures and can range from wrong-site surgery to leaving surgical instruments inside the patient’s body. Factors like fatigue, lack of communication between surgical team members, and inadequate preoperative planning can contribute to surgical errors. For instance, a surgeon performing a procedure on the wrong side of the patient’s body due to a mix-up in patient records.
Diagnostic Errors
Diagnostic errors involve incorrect or delayed diagnoses, which can lead to inappropriate treatment or a lack of treatment altogether. Factors such as cognitive biases, inadequate medical history-taking, and limited access to diagnostic tools can contribute to diagnostic errors. An example of a diagnostic error is a physician misinterpreting test results and providing the wrong diagnosis to the patient.
High-Risk Situations
High-risk situations where medical errors are more likely to occur include shift changes, handoffs between healthcare providers, and transitions of care between different healthcare settings. These transitions are critical points where miscommunication or missed information can lead to errors in patient care.
Implications on Patient Safety
Each type of medical error has its own implications on patient safety. Medication errors can result in adverse drug reactions or medication-related harm, surgical errors can lead to surgical complications or infections, and diagnostic errors can delay necessary treatment or cause harm from unnecessary interventions. Improving patient safety requires addressing the root causes of these errors and implementing strategies to prevent them from happening.
Reporting and Analysis of Medical Errors
Reporting and analyzing medical errors are crucial steps in improving patient safety within healthcare systems. By identifying and understanding errors, healthcare organizations can implement measures to prevent similar incidents in the future.
Importance of Reporting Medical Errors
Reporting medical errors is essential for creating a culture of transparency and accountability in healthcare. It allows for the identification of systemic issues that may be contributing to errors, leading to the implementation of targeted solutions to enhance patient safety.
Challenges in Reporting Medical Errors
- Fear of repercussions or blame from colleagues or superiors
- Lack of standardized reporting procedures
- Concerns about damage to professional reputation
Process of Analyzing Medical Errors
When analyzing medical errors, healthcare professionals typically follow a structured approach to identify root causes. This may involve conducting root cause analysis (RCA) to understand the underlying factors contributing to the error and developing strategies to prevent recurrence.
Utilizing Data for Quality Improvement Initiatives
Healthcare organizations use data from reported errors to track trends, identify common themes, and prioritize areas for improvement. By leveraging this information, organizations can implement targeted interventions to enhance patient safety and overall quality of care.
Patient Safety
Patient safety refers to the measures taken to prevent harm to patients during the provision of healthcare services. It is a critical aspect of healthcare delivery as it ensures that patients receive the highest quality of care without unnecessary risks. Ensuring patient safety is essential in building trust between healthcare providers and patients, as well as in improving overall healthcare outcomes.
Role of Healthcare Providers
Healthcare providers play a crucial role in ensuring patient safety. They are responsible for implementing protocols and procedures that minimize the risk of medical errors and adverse events. This includes proper medication administration, accurate patient identification, effective communication among healthcare team members, and adherence to infection control practices. By staying updated on best practices and continuously improving their skills, healthcare providers can significantly contribute to enhancing patient safety.
Patient Safety Culture Influence
Patient safety culture refers to the attitudes, beliefs, and values that healthcare organizations and their staff have regarding patient safety. A positive patient safety culture promotes open communication, transparency, and a willingness to learn from mistakes. On the other hand, a negative patient safety culture can lead to a lack of accountability, poor teamwork, and increased chances of medical errors.
By fostering a culture that prioritizes patient safety, healthcare organizations can create an environment where errors are less likely to occur.
Best Practices for Promoting Patient Safety
- Implementing standardized protocols and checklists to ensure consistency in care delivery.
- Encouraging open communication among healthcare team members to facilitate the sharing of information and insights.
- Providing regular training and education on patient safety practices and procedures.
- Involving patients in their care by promoting shared decision-making and empowering them to ask questions and raise concerns.
- Conducting regular audits and assessments to identify areas for improvement and implement necessary changes.
In conclusion, the importance of addressing medical errors and prioritizing patient safety cannot be overstated. By implementing best practices and fostering a culture of safety, healthcare organizations can significantly reduce the occurrence of errors and enhance the quality of care provided to patients.
FAQ Compilation
What are some common causes of medical errors?
Common causes include communication breakdowns, medication mix-ups, fatigue among healthcare staff, and system failures.
How do healthcare organizations use data from reported errors?
Healthcare organizations analyze reported errors to identify root causes, implement quality improvement initiatives, and prevent similar errors in the future.





